Recently, our graduate student, Liang Zhiwei from the class of 2021, published an academic paper as the first author in the prestigious journal "IEEE/Optica Journal of Lightwave Technology (JLT)" (indexed in the first zone of Chinese Academy of Sciences, a top-tier journal) in the field of optics/optical communication. This work was completed through collaboration between Hefei University of Technology and Eindhoven University of Technology in the Netherlands. Associate Professor Chen Bin served as the corresponding author, with our school's faculty member, Lei Yi from the School of Computer and Information Science, and Assistant Professor Gabriele Liga and Professor Alex Alvarado from Eindhoven University of Technology, as co-authors. This paper marks the first instance of our school's student publishing a paper as the first author in the IEEE/Optica JLT journal.
The IEEE/OSA Journal of Lightwave Technology, founded in 1983, is jointly published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the Optical Society of America (OSA). It primarily publishes theoretical and experimental papers on topics such as fiber optics and cable technology, active and passive waveguide devices, integrated optics and optoelectronics, transmission systems and subsystems, optical networks, and switching. It is an international top-tier journal in the field of optical communication.
The paper addresses the challenge of accurately and rapidly calculating Kerr nonlinear effects in high-capacity optical communication. Starting from perturbation theory to solve the nonlinear Schrödinger equation, it proposes a more universal analytical model for nonlinear crosstalk. Compared to existing models, the proposed model not only applies to any dual-polarization quadrature amplitude modulation format but also considers all major nonlinear crosstalk terms in the nonlinear channel, as shown in Figure 1.
Compared to traditional numerical methods based on distributed Fourier transform, this model offers significant complexity advantages, greatly reducing computational complexity while ensuring the accuracy of nonlinear noise estimation. Research results show that after long-distance transmission with multiple spans, the estimation error of the proposed 4D model for nonlinear noise power is only 0.15 dB, as shown in Figure 2. The paper also further explores the mechanism of nonlinear interaction between signals and noise in optical transmission, further enhancing the accuracy of estimating the performance of long-distance optical communication transmission.
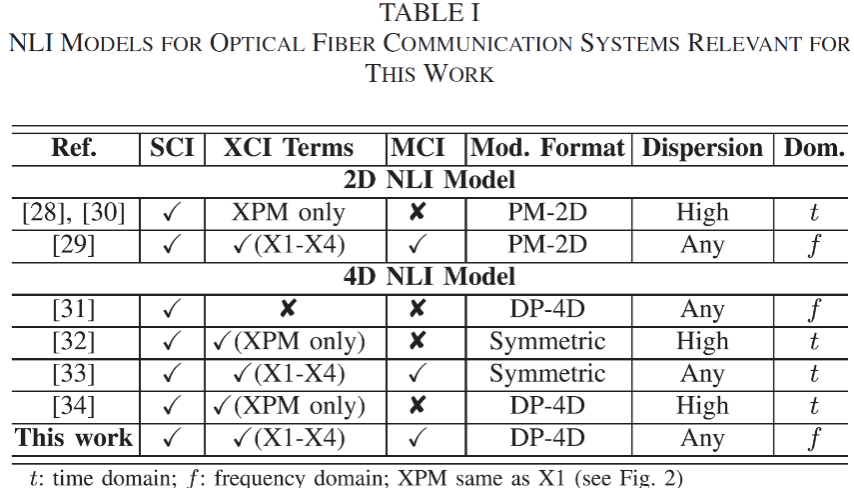
Figure 1: The primary advantages of the nonlinearcrosstalk model proposed in this work
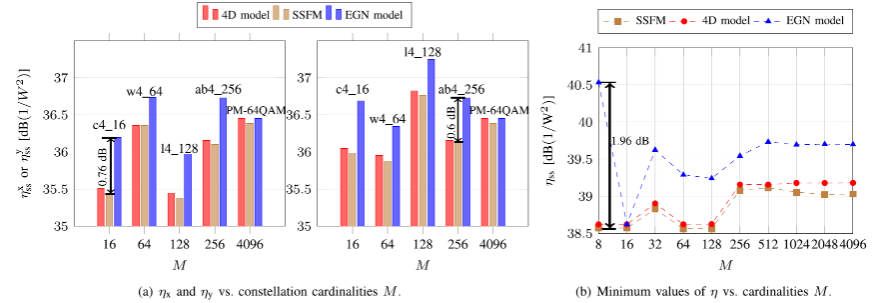
Figure 2: The proposed 4D nonlinear noise model in wavelength-division multiplexing optical transmission systems significantly improves noise estimation accuracy.
 TOP
TOP